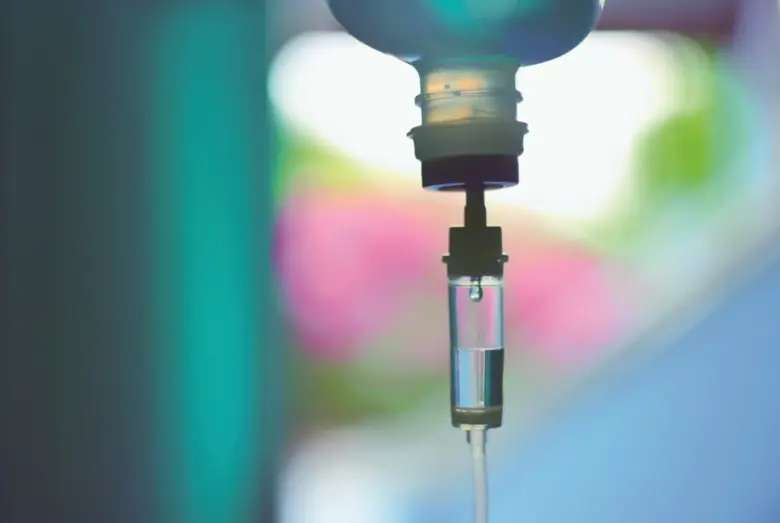
In a major move towards patient safety, the Health Department of Punjab has issued an urgent order to halt the use of six widely utilized medicines. The directive was circulated throughout the state’s health facilities on Sunday, instructing immediate compliance from hospitals, clinics, and pharmacies.
Background to the Ban
The ban came following growing concerns over the safety and quality of several injectable solutions and IV fluids frequently prescribed in routine medical care. Health officials explained that recent clinical evaluations highlighted multiple adverse reactions and inconsistencies in treatment outcomes associated with these medicines.
Medicines Under Prohibition
The issued order lists six specific drugs whose usage is to be stopped with immediate effect:
-
Normal Saline (Sodium Chloride Injection 200ml)
-
DNS Solution (Dextrose Normal Saline 0.9% Sodium Chloride)
-
Dextrose Injection
-
Ringer’s Lactate Injection
-
Bupivacaine Solution (local anesthetic)
-
NS/Dextrose 5% IV infusion
Each of these medications plays a critical role in patient hydration, anesthesia, and intravenous therapy, making the announcement highly impactful across medical practices.
Instructions for Healthcare Providers
Department officials have mandated that doctors, nurses, and hospital staff immediately cease administering these drugs. All healthcare providers are required to submit records of existing stocks and recent usage to district health authorities. The scrutiny encompasses both government and private institutions to ensure thorough compliance and patient safety.
Authority’s Statement & Next Steps
A senior official from the Punjab Health Department said, “This measure is being taken in the best interest of patient health and public safety. Investigations are ongoing, and further instructions regarding alternative medicines and future usage will be communicated to all concerned parties.”
Local pharmacies and medical suppliers have also received notifications, instructing them to halt the sale of the restricted medicines and cooperate fully with regulatory agencies. Outreach initiatives are underway to inform patients about the changes and guide them on alternative treatment options.
Implications for Medical Practice
While alternatives remain available for most applications, medical professionals are advised to exercise heightened caution and consult updated department recommendations before prescribing substitute drugs for patients previously reliant on the banned formulations.
Note: This article describes a developing story; for continuous updates, readers are advised to follow official communications from the Punjab Health Department.